Kernels
LIBSMM_ACC Kernels
Directory Organization
-
autotuning_properties.jsonProperties of the autotuning procedure, read from DBCSR source code -
gpu_properties.jsonGPU card properties -
smm_acc_common.hFunctionalities common to kernel CUDA/HIP codes -
smm_acc_dnt_base.pyKernel base class -
smm_acc_dnt_ALGORITHM.pyKernel class in python -
smm_acc_dnt_ALGORITHM.hBatched Multiply Kernel CUDA/HIP code -
smm_acc_transpose.hTranspose CUDA/HIP code
Batched Multiplication Kernels
All kernels have following signature:
template <int m, int n, int k, int M, int N, int w, int v, int threads, int grouping, int minblocks >
__global__ void
__launch_bounds__(threads, minblocks)
smm_acc_dnt_ALGORITHM
(const int *__restrict__ param_stack, const int stack_size,
const double* __restrict__ a_data, const double* __restrict__ b_data, double* c_data);
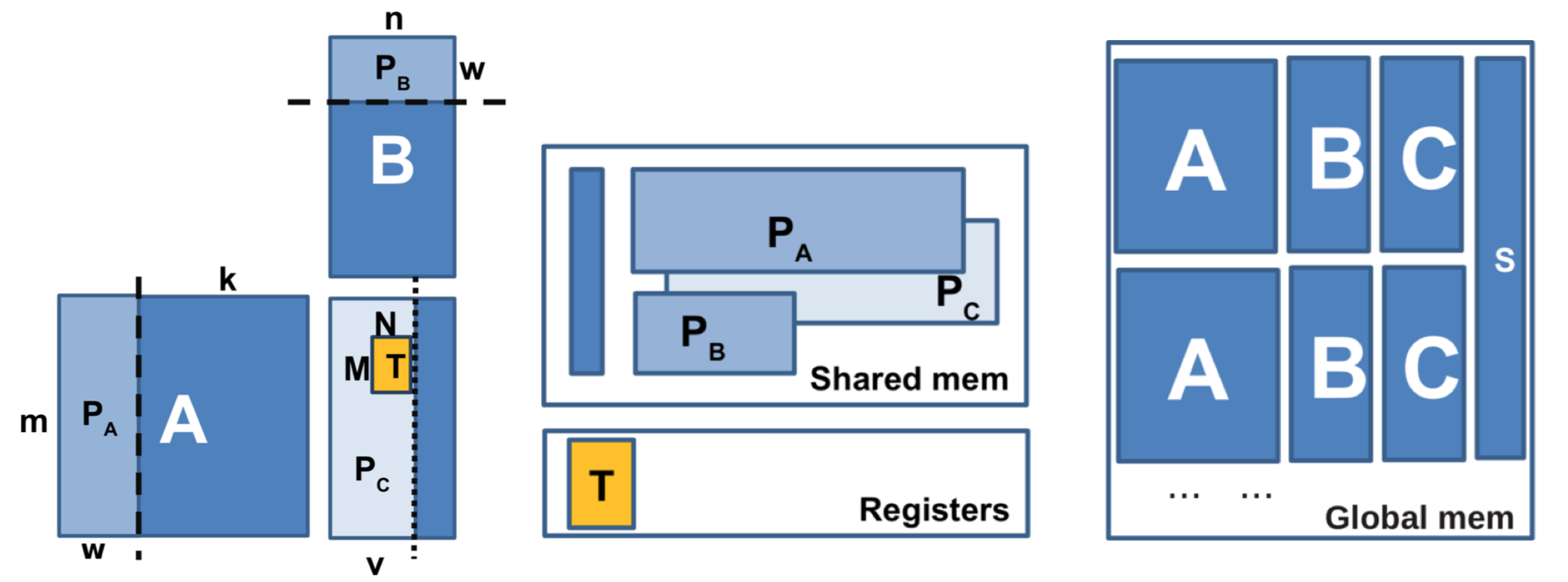
At kernel launch time, the A, B, and C matrices, as well as the product descriptors (the so-called stacks) are all located in global memory on the GPU. Each entry in the stack describes one matrix-matrix product: it contains three pointers to the blocks in the A, B, and C matrices. After the kernel has read a stack entry, it fetches the blocks in matrices A and B from global to shared memory, and updates the C matrix with the product of A and B.
libsmm_acc provides 5 different kernels for this operation (tiny, small, medium, largeDB1, largeDB2), which are optimized for different block sizes. Please refer to the documentation inside the respective .h files for more details.